Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) is a type of peripheral vascular disease. PAD is a serious circulatory condition where clogged or narrowed arteries cause poor circulation to the arms, legs, brain or kidneys. It occurs most often in the lower extremities, causing decreased blood flow to the legs and feet. Just like buildup in the heart, clogged arteries in the lower extremities can cause a stroke or heart attack.
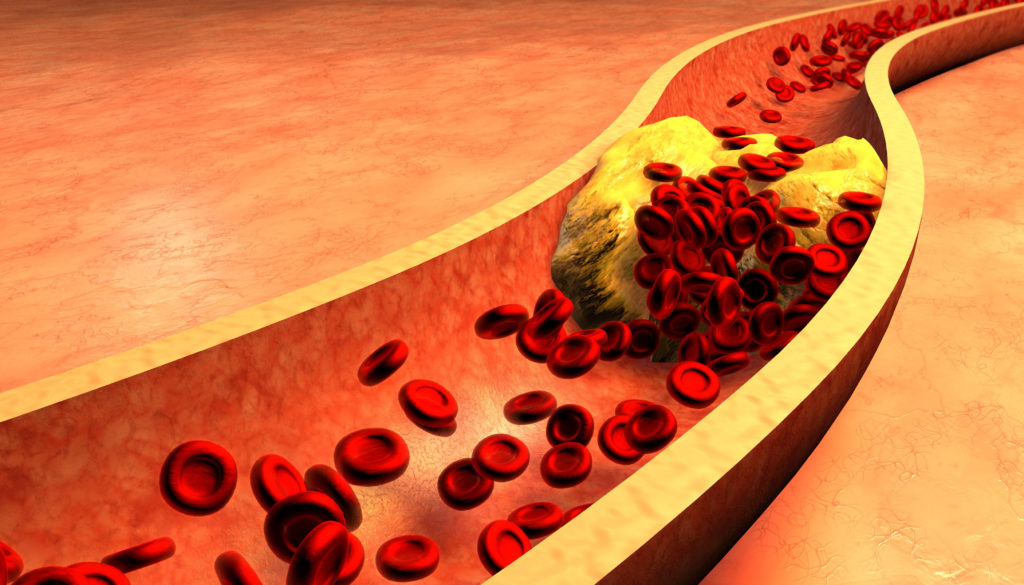
of PAD is fatal within a 5-year period
PAD Risk Factors
The most common risk factors for PAD include:
- age (70+)
- tobacco use
- diabetes (Type 1 and Type 2)
- hypertension (high blood pressure)
- hyperlipidemia (high cholesterol)
- family history of vascular disease

PAD Symptoms

PAD Prevalence
Twenty million Americans have PAD and, left untreated, PAD is fatal 30% of the time within a five-year period.
Fortunately, today there is a non-invasive technology that can determine the presence of PAD: PADnet and PADnet Xpress are PAD diagnostic testing systems that can be completed in 2 to 20 minutes during a regular office visit.
For patients with increased risk factors, including those being 65 years of age or older with a history of diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol or smoking, being informed about this arterial disease is especially essential. Leg pain and discoloration of the toes or feet are possible symptoms of PAD. It is important to note, however, that many people with PAD do not experience any symptoms. Testing can help determine if you have PAD and whether medical or surgical treatment is necessary.